Before packing, check this list of items prohibited from entering a particular country or region.
Key takeaways
- A green card (or Permanent Resident Card) is an identity document that allows non-US citizens to live and work in the United States permanently.
- To get a green card, you must receive family or employment sponsorship, win the green card lottery, or be granted asylum status.
- The green card application process requires you to file an appropriate petition and await a decision from the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
- The green card lottery (or Diversity Visa Lottery) is an annual program that provides between 50,000 and 55,000 immigrant visas to randomly selected individuals from countries with low immigration rates to the US.
What is a green card?
A green card, officially called a Permanent Resident Card, is an identity document issued by US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) that allows non-American citizens to move to the United States and live and work there permanently.
This card proves an individual's legal status as a permanent resident, granting them various rights and responsibilities. Green card holders can enjoy benefits such as the ability to work, access certain social services, and apply for US citizenship after meeting specific requirements.
Immigrants can get a green card through various pathways, including family sponsorship, employment opportunities, refugee or asylum status, and the Diversity Visa lottery.
How to get a green card in USA without marriage?
To get a green card in USA without marriage, there are several pathways, including applying for employment sponsorship, entering the Diversity Visa lottery, and seeking asylum status. Each route requires meeting specific eligibility criteria and completing the necessary application processes with US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).

The Diversity Visa (DV) lottery provides 50,000 green cards annually...
How to get a green card
To get a green card, there are several pathways, each with its own requirements and procedures, including family sponsorship, employment sponsorship, and selection via the Diversity Visa (DV) lottery.
Here are further details on how to secure permanent residency in the United States:
Family sponsorship:
US citizens and permanent residents can sponsor certain family members for a green card. Eligible relatives include:
- Spouses
- Unmarried children under 21
- Parents (for US citizens over 21)
- Siblings (for US citizens over 21)
The process involves filing a petition with US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) and proving the family relationship, for example, by providing copies of a birth or marriage certificate.
Employment sponsorship:
American employers can sponsor immigrants based on the workers' skills and job qualifications. Below are the eligible categories:
- EB-1: for individuals with extraordinary abilities in science, art, education, business, or athletics or are internationally recognised professors/researchers or multinational executives.
- EB-2: professionals with advanced degrees or exceptional abilities.
- EB-3: skilled workers, professionals, and other workers performing tasks for which qualified employees are unavailable in the United States.
- EB-4: special immigrants, including religious workers and employees of US foreign service posts.
- EB-5: investors who help finance a new commercial enterprise that creates jobs for American workers.
Diversity Visa (DV) lottery:
The Diversity Visa (DV) lottery provides between 50,000 and 55,000 green cards annually to individuals from countries with low immigration rates to the US. Applicants are selected through a random lottery system and must meet basic eligibility requirements, such as having a minimum of a high school degree or qualifying work experience.
Asylum or refugee status:
Individuals granted asylum or refugee status due to persecution in their home country can apply for a green card after being physically present in the United States for at least one year.
Other green card pathways:
There are additional special categories and circumstances under which immigrants might be eligible for a green card, including:
- Special immigrant juveniles: children who have been abused, neglected, or abandoned.
- US citizens' widow(er)s: widows or widowers of US citizens.
- Victims of abuse: under the Violence Against Women Act (VAWA), certain abused spouses, children, and parents of US citizens or permanent residents can self-petition for a green card.

What does a green card look like?
A green card looks like a wallet-sized plastic identification card featuring several distinctive elements to establish identity and prevent fraud.
Below is a diagram of a green card, followed by an explanation of each field.
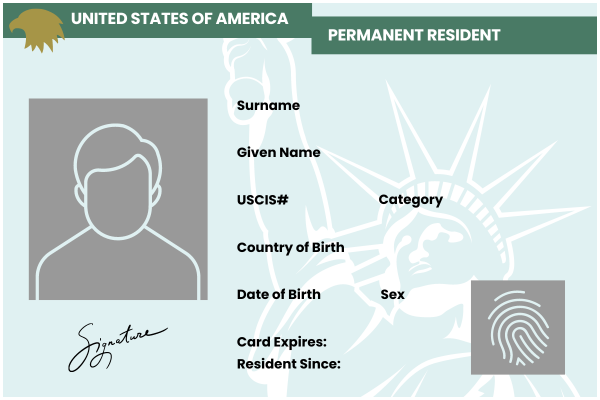
- Photo: a full-face photograph of the cardholder taken within the last six months against a plain background.
- Surname and Given Name: the cardholder's full name.
- USCIS Number: a unique 7-9 digit number assigned by US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). It's also called an A-Number or Alien Number.
- Category Code: a code that indicates the category under which the green card was issued (e.g., IR1 for an immediate relative of a US citizen).
- Country of Birth: the country where the cardholder was born.
- Date of Birth: the cardholder's birth date.
- Sex: the gender of the cardholder.
- Card Expires: the date the green card expires (typically, validity lasts 10 years for permanent residents or 2 years for conditional residents).
- Resident Since: the date the green card was issued.
On the back of the card is the USCIS seal and a magnetic strip or barcode containing encoded information about the cardholder.
Other security features to ensure the document's authenticity include:
- Intricate guilloche patterns that are difficult to replicate,
- Colour-shifting ink,
- A holographic image,
- An embedded microchip that contains information about the cardholder that's only readable using a special device.

How to prepare for a green card interview?
Preparing for your green card interview is crucial to ensure a smooth application process and increase your chances of success.
Here's how to get yourself ready for the big day:
Documents to bring:
- The interview appointment notice sent to you by USCIS or the US consulate.
- Your current, valid passport.
- If applying from within the United States, a copy of your Form I-485 (Application to Register Permanent Residence or Adjust Status).
- If applying from overseas, the confirmation page of Form DS-260 (Immigrant Visa and Alien Registration Application).
- A copy of your petition's approval notice.
- Your medical examination report and vaccination record in a sealed envelope.
- Proof of identity such as a birth certificate or national ID card.
- If you're applying for a green card based on marriage, provide your marriage certificate and evidence of your relationship, e.g., communication records, photos, joint bank account statements, or affidavits from friends and family.
- If you're applying through employment, provide your job offer letter, pay stubs, and tax returns.
- A copy of your visa, I-94 arrival/departure record, and any other immigration documents.
- Form I-864, Affidavit of Support, and any other financial documents such as tax returns, pay stubs, and bank statements.
- For consular processing, bring police certificates from all countries where you have lived for more than six months since age 16.
Common green card interview questions:
For family-based green cards:
- How did you meet your spouse?
- When and where did you get married?
- Can you describe your wedding ceremony?
- Where do you live, and who else lives with you?
For employment-based green cards:
- What is your job title, and what are your responsibilities?
- Can you describe a typical workday?
- How long have you been employed with your current employer?
- What are your qualifications for this position?
General questions:
- Can you tell me about your educational background?
- Have you ever been arrested or convicted of a crime?
- Have you ever violated US immigration laws?
- What are your plans if you receive your green card?
Tips for the interview:
- Always answer truthfully. Misrepresentation can lead to denial of your application and future immigration benefits.
- Review common questions and practice your answers with a friend or family member.
- Wear business or business casual attire to present yourself professionally.
- Take deep breaths and stay calm during the interview. It's normal to be nervous, but try to remain composed!

Green card application process
The green card application process involves a series of steps that vary depending on the eligibility category under which you are applying.
Here is a comprehensive overview of the general application process:
1. Determine your eligibility:
First, work out which category you qualify for, e.g. family or employment sponsorship, selection through the annual Diversity Visa lottery or being granted asylum or refugee status.
2. File the appropriate petition:
Next, establish your eligibility for a green card by filing a petition — note this form differs depending on your qualifying category:
- Family-based sponsorship: the sponsor files Form I-130 (Petition for Alien Relative).
- Employment-based sponsorship: the employer files Form I-140 (Immigrant Petition for Alien Worker).
- Special categories: different forms will be required, such as Form I-360 for Special Immigrants.
3. Wait for a visa number:
Immediate relatives such as spouses, parents, and unmarried children under 21 of US citizens do not need to wait for a visa number. However, those who fall into the family and employment-based categories must wait and check USCIS's monthly Visa Bulletin.
4. File for "adjustment of status" or "consular processing":
Once a visa number is available (if applicable), you must either:
If in the US, file Form I-485 (Application to Register Permanent Residence or Adjust Status) with USCIS. You must also schedule a biometrics appointment where your fingerprints, photograph, and signature will be taken;
OR,
If outside the US, apply for an immigrant visa through an American embassy or consulate in your home country, submit Form DS-260 (Online Immigrant Visa Application), and attend an interview, during which you must provide additional documentation and answer questions to verify your eligibility.
5. Receive a decision:
After your interview and the review of your application, you will get one of the following decisions:
- Approved: you will receive your green card in the mail if you applied through the "adjustment of status" process. If you applied through "consular processing", you will receive an immigrant visa that allows you to enter the US as a permanent resident, and your green card will be mailed to your new address in the States after entry.
- Request for Additional Evidence (RFE): if more information is needed, you will receive an RFE and must provide the requested documents.
- Denied: you will receive a notice explaining the reasons and information on whether you can appeal the decision.
Other green card application requirements:
- A medical examination by an authorised physician.
- In family-based cases, the sponsor must prove they can financially support the applicant by filing Form I-864 (Affidavit of Support).
- Various fees for filing petitions, sending applications, and completing biometric services.
How long does it take to get a green card?
To get a green card takes, on average,*
1-2 years
*Note that family-based green cards for non-immediate relatives can take over 10 years to process.
What is the Visa Bulletin?
The Visa Bulletin is a monthly publication from the US Department of State that provides information on the availability of immigrant visa numbers. It shows the priority dates currently being processed for various family and employment-based visa categories, indicating when applicants can proceed with their green card applications.
This bulletin helps applicants determine when they can file for adjustment of status or consular processing based on their category and country of origin. It's also an essential tool for those waiting for their priority date to become current so they can advance in the immigration process.

Entry is free, but always apply via the official DV lottery website and avoid scammers...
What is the green card lottery?
The green card lottery, officially known as the Diversity Visa (DV) lottery, is an annual program administered by the US Department of State to diversify the immigrant population and promote multiculturalism in the United States. It provides between 50,000 and 55,000 immigrant visas each year to randomly selected individuals from countries with low immigration rates to the States, offering them permanent residency and a chance to start a new life overseas.
Green cards granted through the lottery are distributed among six geographic regions (Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America, North America and Oceania), and no one country may receive more than 7% of the available green cards in any year.
While the list of eligible countries changes each year, Canada, China, the Dominican Republic, El Salvador, India, Jamaica, Mexico, the Philippines, South Korea, Taiwan and the UK (excluding Northern Ireland) have been ineligible for the DV lottery since its inception in 1995 due to high migration rates to the US.
Entry is free, but always apply via the official DV lottery website and avoid scammers asking for money in exchange for inaccurate advice on how to win.
What are the chances of winning a green card?
The chances of winning a green card are approximately 0.25% (or 1 in 400), assuming that 55,000 green card lottery winners are selected from a pool of 22.2 million applicants.
While winners are chosen at random, the best way to increase your odds is by following all instructions carefully and accurately filling out your application to prevent automatic rejection, including ensuring:
- Your personal details are correct and match your official documents,
- Your photo is recent, unaltered and follows official guidelines,
- You submit your application early in the registration period, minimising the risk of encountering technical difficulties on the DV Lottery website due to high traffic closer to the deadline.
Also, avoid submitting multiple entries, as this will result in automatic disqualification.

Source: Financial Express

How to apply for the green card lottery
To apply for the green card lottery, follow our step-by-step guide:
1. Check eligibility
Ensure you meet the eligibility criteria below:
- You are a native of an eligible country with low immigration rates to the United States (do note that this list might change each year).
- You have at least a high school education or equivalent, or two years of work experience within the past five years in an occupation that requires at least two years of training or experience.
2. Submit an online entry
To complete your application, go to the official US Department of State's DV lottery website during the registration period, typically from early October to early November.
Then, fill out the Electronic Diversity Visa Entry Form (DS-5501) — information you will need to provide includes personal details, education or work experience, and a recent photograph that meets the specified requirements. Double-check the form to ensure accuracy, and hit submit.
You will receive a confirmation number, which you should save and keep safe, as it is essential for checking the status of your entry.
3. Check your status
The green card lottery results are announced in May of the following year. You can check your entry status using your confirmation number on the DV lottery website.
If you are selected, follow the instructions on the website, including submitting additional documents, undergoing a medical examination, and attending an interview at a US embassy or consulate.
4. Prepare for the interview
Before your interview, gather your birth certificate, passport, police certificates, and other supporting materials, and submit an Online Immigrant Visa Application (DS-260) form. And don't forget to prepare answers for questions about your eligibility, such as:
- Why do you want to immigrate to the US?
- How will you support yourself and your family once you arrive?
- Do you plan to return to your home country?
5. Receive your visa and move to the States
If your interview is successful, you will be granted an immigrant visa, which allows you to enter the country as a permanent resident within the visa validity period. Your green card will then be mailed to your new address in the US of A.
How to get a green card fast
To get a green card fast is challenging due to the complex and often lengthy US immigration process. However, one of the fastest pathways is through family sponsorship by an American citizen.
Immediate relatives, such as spouses, unmarried children under 21, and parents, are given priority and do not have to wait for a visa number to become available, making this one of the quickest routes. Additionally, Americans can bring their foreign fiancé(e) to the States on a K-1 visa, allowing them to marry and then adjust their status to obtain a green card.
How long does a green card last?
A green card lasts
10 years
after this, you will need to follow the renewal process.

How do green card holders become citizens?
Green card holders become citizens through a process called naturalisation. However, there are a few requirements you must meet to be eligible:
- You must have been a permanent resident for at least 5 years or 3 years if you are married to a US citizen.
- You must have been physically present in the States for at least 30 months out of the 5 years (or 18 months out of the 3 years).
- You must have continuously resided in the US and not had any trips abroad over six months.
- You must demonstrate good moral character, which generally means abiding by American laws and not having a serious criminal record.
To apply to become a fully-fledged American, you must first complete Form N-400 (Application for Naturalisation) with US Citizenship and Immigration Services. Then, schedule a biometrics appointment and attend a naturalisation interview, during which a USCIS officer will ask questions about your application and background.
You must also take a civics test covering US history and government and a basic English test (unless you qualify for an exemption based on age, residency duration, or disability). Questions might include:
- What are two rights in the Declaration of Independence?
- Name your US Representative
- Why did the colonists fight the British?
If you pass the interview and tests, USCIS will schedule you for an oath ceremony, where you will take the Oath of Allegiance to the United States. After which, you will receive a Certificate of Naturalization, which proves your new status as a US citizen.
As an American, you gain the right to vote, obtain a US passport, and enjoy other benefits reserved for citizens, such as the ability to sponsor relatives for immigration.

Green card renewal explained
To maintain your status as a permanent resident in the United States, your green card needs to be renewed every 10 years, and you must start the process six months before your card expires.
However, if it has been lost, damaged, or stolen, request a replacement immediately.
Follow the steps below for a smooth renewal:
1. Complete Form I-90 (Application to Replace Permanent Resident Card)*:
You can either file this form online through the USCIS website or download it and fill it out by hand, then mail it to the address provided in the form instructions.
2. Pay the renewal fees:
These costs include a filing (check the USCIS website for the current amount and note that some applicants may qualify for a fee waiver) and fees for biometric services, such as fingerprinting.
3. Submit supporting documents:
Provide a copy of your current green card and any additional documents requested by USCIS, such as a police report for a lost or stolen card.
After you apply for a green card renewal, you will receive a receipt notice confirming your application and be scheduled for a biometrics appointment. If approved, your new green card will be mailed to you — processing times can vary, so check the USCIS website for current timelines.
*Note that if you have a conditional green card (valid for 2 years), you must file Form I-751 (Petition to Remove Conditions on Residence) instead of Form I-90.